Deep Brain Stimulation
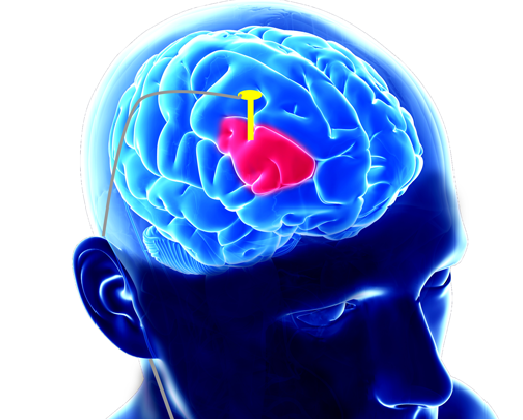
Deep Brain Stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical impulses. It is used to decrease the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulties with movement.
Q: What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson's disease?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical impulses. It is used to decrease the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulties with movement.
Q: How does Deep Brain Stimulation work for Parkinson's disease?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation works by modulating abnormal electrical signals in the brain associated with Parkinson's disease. The electrodes implanted in the brain deliver high-frequency electrical impulses to specific regions, such as the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus, which helps regulate and restore normal brain activity.
Q: Who is a suitable candidate for Deep Brain Stimulation?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation is typically recommended for people with Parkinson's disease who have not responded well to medication or who experience significant medication-related side effects. Candidates usually have advanced Parkinson's disease and experience motor symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life.
Q: What are the potential benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's disease?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation can provide significant improvement in motor symptoms, including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and dyskinesias (involuntary movements). It may also reduce medication dosage and improve overall quality of life for some individuals.
Q: What are the risks and potential complications associated with Deep Brain Stimulation?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation is generally considered safe, but it does carry certain risks. Potential complications include infection, bleeding in the brain, electrode misplacement, cognitive changes, speech or swallowing difficulties, and device-related problems. However, these risks are relatively low and can be managed by an experienced surgical team.
Q: What is the recovery process like after Deep Brain Stimulation surgery?
A: The recovery process after Deep Brain Stimulation surgery usually involves a hospital stay of a few days. Initially, there may be some swelling and discomfort at the surgical site. Over time, as the brain adjusts to the stimulation, improvements in symptoms can be observed. It's important to follow the post-operative care instructions provided by the medical team.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes or restrictions after Deep Brain Stimulation?
A: While there are no specific lifestyle changes or restrictions, individuals with Deep Brain Stimulation need to be mindful of certain considerations. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor and adjust the stimulation settings. Some activities, such as undergoing MRI scans, may require precautions due to the implanted device. It is advisable to discuss any specific concerns with the medical team.
Q: Can Deep Brain Stimulation completely cure Parkinson's disease?
A: Deep Brain Stimulation does not cure Parkinson's disease. It is a treatment that helps manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with the condition. The underlying neurodegenerative process of Parkinson's disease continues, but DBS can significantly improve quality of life for many individuals.
Q: Are there alternative treatments to Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's disease?
A: Yes, there are alternative treatments for Parkinson's disease, including medication therapies and other surgical options such as lesioning procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the individual's condition, preferences, and response to other therapies. A movement disorder specialist can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend the most suitable treatment approach.