Neuro-Oncology

Neurooncology is a branch of medicine that concerns cancers of the brain and spinal cord. Cancers of the nervous system are often severe conditions that eventually become life-threatening.
Q: What is a brain tumor?
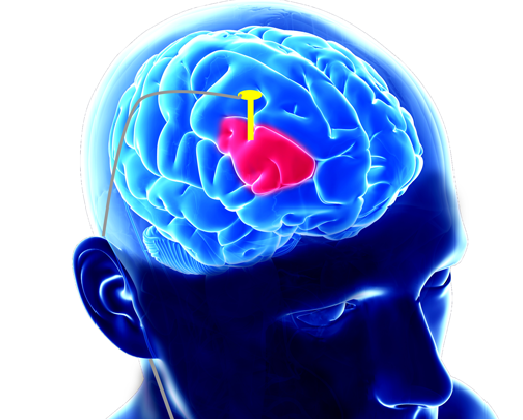
A: A brain tumor is an abnormal growth or mass of cells in the brain. It can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can originate from the brain itself (primary tumor) or spread from other parts of the body (metastatic tumor).
Q: What are the common symptoms of a brain tumor?
A: The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary depending on its size, location, and rate of growth. Common symptoms may include headaches, seizures, changes in vision or hearing, cognitive and memory problems, balance and coordination difficulties, nausea and vomiting, and personality or behavioral changes.
Q: How are brain tumors diagnosed?
A: Brain tumors are diagnosed through a combination of medical history evaluation, neurological examination, and imaging tests such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans. A biopsy may also be performed to determine the type of tumor and its grade.
Q: What are the treatment options for brain tumors?
A: Treatment options for brain tumors depend on several factors, including the type, size, location, and grade of the tumor. Treatment may involve surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, or a combination of these approaches. The treatment plan is personalized to each individual's case.
Q: Can brain tumors be cured?
A: The prognosis and potential for a cure depend on the type and grade of the brain tumor, its location, and the overall health of the patient. Some benign brain tumors can be completely cured with surgical removal, while malignant tumors may require a combination of treatments and ongoing management.
Q: What are the possible risks and complications associated with brain tumor treatment?
A: The risks and complications of brain tumor treatment depend on the specific treatment methods used. Surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding brain tissue. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can have side effects. The medical team will discuss potential risks and complications before initiating treatment.
Q: Can brain tumors recur after treatment?
A: Brain tumors can recur after treatment, even if they have been surgically removed or treated with other therapies. The likelihood of recurrence depends on several factors, including the type and grade of the tumor, the extent of the initial treatment, and individual factors. Regular follow-up visits and imaging scans are important to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Q: What supportive care is available for individuals with brain tumors?
A: Supportive care for individuals with brain tumors focuses on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and providing psychological and emotional support. Supportive care may include pain management, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, counseling, and support groups.
Q: Are there any new advancements or promising treatments for brain tumors?
A: Research in brain tumor treatment is ongoing, and there are constant advancements in understanding the biology of brain tumors and developing new treatment approaches. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and personalized medicine approaches. Clinical trials may be available for eligible patients to access novel treatments.
Q: How important is early detection in improving the prognosis for brain tumors?
A: Early detection of brain tumors is important for improving prognosis and treatment outcomes. Identifying and diagnosing tumors at an early stage can allow for prompt initiation of appropriate treatment, potentially leading to better outcomes and a higher chance of successful treatment. Regular check-ups and timely medical attention for any concerning symptoms are crucial.